There’s a question that comes up constantly in the mushroom community: “I took 1 gram and it hit way harder than when I ate dried mushrooms at the same dose. What gives?”
It’s not your imagination. It’s not a batch that was somehow stronger. It’s not a placebo.
When you consume psilocybin in chocolate form — or in a gummy, or in a capsule — your body processes it differently than it does when you chew through a handful of dried Psilocybe cubensis. The matrix the compound is delivered in changes everything: the onset, the peak, the smoothness, the intensity, and even the duration.
This blog breaks down exactly why 1 gram in a chocolate bar is not the same as 1 gram of raw dried mushrooms — and what that means for how you should approach dosing.
First, Let’s Talk About What Psilocybin Actually Is
Before we get into the chocolate science, a quick primer.
Psilocybin is the compound in magic mushrooms that makes them magic. But here’s the thing — psilocybin itself is technically inactive. It’s what pharmacologists call a prodrug. When you ingest it, your body converts it into psilocin, the compound that actually binds to your serotonin receptors and produces the psychedelic experience.
This conversion happens primarily in the liver through a process called dephosphorylation. The speed and completeness of that conversion — and how efficiently psilocin enters your bloodstream — is where the differences between consumption methods start to emerge.
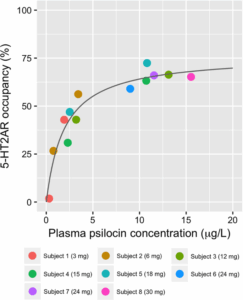
Pharmacokinetic research shows that after oral administration, psilocybin is detectable in the bloodstream within 20 to 40 minutes, with psilocin peak levels typically arriving between 1 and 3 hours depending on the individual and method of consumption. But that window shifts significantly depending on what vehicle is carrying the psilocybin into your body.
If you want a broader overview of how psilocybin affects you once it’s in your system, our guide on How Shrooms Make You Feel is a great foundation.
The Real Reason Dried Mushrooms Are Harder to Digest Than You Think
Here’s something most people don’t think about: when you eat dried mushrooms, you’re not just eating psilocybin. You’re eating an entire organism — cell walls, fibres, proteins, polysaccharides, and all.
The cell walls of fungi are made of chitin (pronounced “KYE-tin”) — the same tough structural compound found in crab shells and insect exoskeletons. Chitin is notoriously difficult for the human body to break down. Your digestive system doesn’t produce the enzymes needed to fully dissolve it, which means two things happen when you eat raw dried mushrooms:
- Absorption is delayed and inconsistent. Psilocybin locked inside intact chitin cell walls takes longer to escape into your digestive system, leading to a slower, more unpredictable onset.
- Nausea is common. Chitin irritates the gastrointestinal tract. It triggers inflammatory and immune responses in the gut, which contributes to the infamous “gut rot” that many mushroom users experience in the first 30–60 minutes of a trip.
As mycologist Paul Stamets has noted, “raw mushrooms are largely indigestible because of their tough cell walls, mainly composed of chitin.” Raw mushrooms may even contain heat-sensitive compounds and pathogens that the body tries to expel — which is part of why nausea can be intense with unprocessed dried material.
This is the foundational reason why edible forms of psilocybin — chocolates, gummies, capsules, and teas — can feel so different. They bypass or reduce the chitin problem entirely.
What Happens When Mushrooms Are Processed Into Chocolate
When mushrooms are prepared for a chocolate bar, the process typically involves grinding the dried mushrooms into a fine powder and incorporating that powder into a chocolate matrix. This matters for several reasons.
1. Cell Wall Disruption Increases Bioavailability
Grinding dried mushrooms into a powder mechanically ruptures the chitin cell walls that normally slow absorption. More surface area is exposed, which means psilocybin leaches out into your digestive system more quickly and more completely than it would from a whole or coarsely chewed mushroom.
2. Fat Content in Chocolate Affects Absorption Timing
Chocolate contains significant amounts of fat — primarily cocoa butter. Fats slow gastric emptying, which means the contents of your stomach move more gradually into your small intestine (where most absorption occurs). This produces a classic edible effect: a delayed onset followed by a more sustained, even release of the active compound.
The fats and sugars in the chocolate matrix can slow gastric emptying, potentially delaying initial effects while extending overall duration. This is why many people describe mushroom chocolate experiences as having a softer, more gradual come-up compared to eating raw dried mushrooms — which tend to hit harder and faster on an empty stomach.
3. Gummies Are Different Again
Gummies add another layer of distinction. Many high-quality mushroom gummies are made with psilocybin extract rather than ground whole mushroom matter. This means there’s no chitin to deal with at all — just the active compound in a gelatin or pectin delivery matrix.
Gummies often contain just psilocybin extract and no mushroom matter, which is why you generally shouldn’t experience the nausea or muscle cramps that can come with raw mushroom consumption. The tradeoff is that without the full spectrum of compounds found in whole mushrooms, you may lose some of the entourage effects that whole-fruiting-body consumption provides.
The Stomach Environment and Why It Changes Everything
One factor almost nobody talks about when comparing edible formats is the role of stomach acidity and fullness at the time of consumption.
Psilocybin conversion to psilocin happens largely in the liver — but the speed at which psilocybin reaches the liver depends heavily on how quickly it moves through your stomach. An empty, acidic stomach is a very different environment than one that’s full and buffered by fats and carbohydrates.
- Empty stomach + dried mushrooms: Fast gastric emptying, chitin irritation, potentially intense and fast onset with significant nausea risk.
- Full stomach + mushroom chocolate: Slowed gastric emptying due to fat and sugar content, longer onset (sometimes 90 minutes to 2 hours), smoother peak, reduced nausea.
- Empty stomach + mushroom chocolate: Faster than full-stomach chocolate, still smoother than raw dried mushrooms due to powder format and lack of raw fungal matter.
This is critical for dosing. If you ate 1 gram of dried mushrooms on an empty stomach last time and now you’re eating 1 gram of mushroom chocolate after a meal — you are having a fundamentally different pharmacokinetic experience, even at the same gram weight.
The Cacao Chemistry: Why Chocolate Isn’t Just a Delivery Vehicle
Here’s where things get genuinely fascinating. Chocolate isn’t just a neutral wrapper for psilocybin. The cacao itself is pharmacologically active — and it may directly potentiate the effects of psilocybin.
Cacao as a Mild MAOI
Cacao contains naturally occurring compounds called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Specifically, research has identified tetrahydro-beta-carbolines in cacao — compounds that slow the breakdown of tryptamine alkaloids, including psilocin, in the body.
MAO (monoamine oxidase) is an enzyme responsible for breaking down serotonin and other neurotransmitters — including psilocin — in your gut and bloodstream. When MAO activity is reduced, more psilocin survives and remains active for longer. This is the same basic mechanism behind ayahuasca, where the MAOI-containing plant prevents DMT from being broken down before it can produce effects.
Cacao is not a strong MAOI by any means. But in sufficient quantities, it is thought to produce a mild MAOI effect that can potentiate and extend the effects of psilocybin. The Aztecs were almost certainly aware of this synergy — even if they didn’t have the biochemical language to describe it.
Theobromine: The Heart-Opener
Cacao beans contain up to 40–50% fat and are rich in theobromine — one of the main compounds responsible for their uplifting and stimulating properties. Theobromine is a mild stimulant that can complement the energizing aspects of a psilocybin experience, while also acting as a vasodilator — meaning it widens blood vessels and increases blood flow throughout the body, including to the brain.
Anandamide and PEA
Cacao also contains anandamide — sometimes called the “bliss molecule” — a naturally occurring cannabinoid that produces feelings of euphoria by reducing pain, stress, and anxiety. Cacao also contains enzyme inhibitors that slow the breakdown of anandamide in the body, prolonging its effects.
Additionally, cacao contains phenylethylamine (PEA), sometimes called the “love molecule,” which produces stimulant and mood-elevating effects. The combination of theobromine, anandamide, PEA, and mild MAOI activity means that the chocolate in your mushroom bar is not passive — it’s contributing its own pharmacological fingerprint to the experience.
This ancient biochemical synergy is almost certainly why the Aztecs combined these two “foods of the gods” for thousands of years in their ceremonial practice.
The Ancient Aztec Combo: They Knew Before We Did
The combination of cacao and psilocybin mushrooms is not a modern invention. Thousands of years ago, the Aztecs and other Mesoamerican cultures were knowingly combining cacao with the transformative power of psilocybin mushrooms in sacred ceremony. This ancient combination was referred to as “cacahua-xochitl” — literally meaning “chocolate-mushrooms.”
The Aztecs combined psilocybin mushrooms with admixtures containing honey, flowers, and herbs, according to records of Aztec history. During the ceremony, the Aztecs would reportedly drink the cacao first, then eat the psilocybin mushrooms with honey.
We now know that cacao contains small amounts of enzyme inhibitors capable of slowing the breakdown of the psychoactive compounds found in psilocybin mushrooms, thereby perpetuating or amplifying the effects. The Aztecs may not have had the biochemical language — but they had thousands of years of empirical observation.
Dosing Mushroom Chocolates: What 1 Gram Actually Means
So with all of this context — what does 1 gram in a chocolate bar actually mean?
The Potency Variable: What Kind of Mushroom Was Used?
Not all mushroom chocolates are created equal. The psilocybin content of magic mushrooms varies enormously — even within the same species. Psilocybin content typically ranges from around 0.5% to 1% of the dried weight of the mushroom, with a range of 0.03% to 1.78%. A 1 gram bar made with Penis Envy — one of the most potent strains available — will hit dramatically harder than a 1 gram bar made with a lower-potency Golden Teacher or B+ strain.
This is a crucial distinction that many consumers overlook. When a bar says “1g,” that’s the weight of mushroom material — not the weight of psilocybin. The actual psilocybin content depends entirely on which strain was used and how it was cultivated.
Check out our breakdown of magic mushroom strains to understand the potency differences between popular varieties.
Distribution: The Hot Spot Problem
Here’s a dirty secret about homemade and low-quality mushroom chocolates: psilocybin doesn’t distribute evenly through chocolate without proper technique.
When mushroom powder is added to melted chocolate without careful, thorough mixing, the powder can clump and settle in certain areas of the bar. This creates what are sometimes called “hot spots” — sections of the bar with significantly more psilocybin than others. You might eat what you think is one square (a quarter gram) and actually consume the equivalent of two grams — or almost nothing.
Professional manufacturers strive to ensure an even distribution of psilocybin throughout chocolate bars, but amateur producers may create hot spots with concentrated doses in specific pieces. This inconsistency is one of the primary reasons why dosing mushroom chocolates can feel so unpredictable — especially with bars from unverified sources.
The Fat-Delay Factor: Why Timing and Fullness Matter
As we covered above, the fat content in chocolate slows gastric emptying. This means:
- Don’t redose too early. Many people make the mistake of eating a square, waiting 45 minutes, feeling nothing significant, and eating another square — only to have both doses hit simultaneously when gastric emptying finally occurs. This is how people accidentally overwhelm themselves on what they thought was a moderate dose.
- Wait at least 90 minutes before considering a redose. Chocolate edibles can take up to two hours to fully onset depending on your metabolism and what else is in your stomach.
- Your last meal matters. A heavy, fatty meal before your chocolate can delay onset even further. A light meal or empty stomach will bring it on faster and more intensely.
The Cacao Potentiation Factor
If you’re comparing your mushroom chocolate experience to a previous dried mushroom experience at the “same” dose — remember to factor in the cacao chemistry. The mild MAOI activity, theobromine, anandamide, and PEA in the chocolate matrix may be contributing to a noticeably stronger or more euphoric experience even before you account for any absorption or distribution differences.
This is especially relevant with ceremonial-grade or high-cacao-percentage chocolate bases. A 70% dark chocolate bar is going to have more active cacao compounds than a milk chocolate base — and may produce a meaningfully different experience at the same mushroom dose.
Practical Dosing Guidelines for Mushroom Chocolates
For Beginners: Start Lower Than You Think You Need To
If you’re new to mushroom chocolates or edibles in general, start with 0.5g–1g and wait a full 90 minutes before evaluating. The delayed onset of fat-based edibles means you need to be patient. A common beginner mistake is to dose at 1g, feel very little at 45 minutes, eat another gram, and then get hit by 2g all at once.
Recreational doses of psilocybin mushrooms are typically between 1.0 and 3.5–5.0 g of dry mushrooms — but in chocolate form, with the factors we’ve discussed, many people find the lower end of that range produces a fuller experience than expected.
For Experienced Users: Scale Cautiously
Even experienced mushroom users should reduce their expected dose by 10–20% when switching from dried mushrooms to chocolate. The smoother, more even absorption — combined with cacao’s mild potentiation — means the same gram weight often produces a more intense experience in chocolate form.
Source Matters Enormously
Given the real risks of uneven distribution in amateur bars, and the documented presence of undisclosed or mislabelled ingredients in unregulated edibles, sourcing your mushroom chocolates from a trustworthy vendor is not optional — it’s essential.
Browse our full selection of mushroom chocolates and mushroom gummies from Shroom Bros — lab-quality sourcing, reliable potency, and consistent distribution every time.
Consider Microdosing Formats for Precision
If consistent, precise dosing is your primary goal — especially for therapeutic or productivity-focused use — microdose capsules offer the most reliable and measurable format. Capsules eliminate the fat-delay variable, the distribution inconsistency, and the cacao potentiation factor, giving you a cleaner baseline from which to calibrate your experience.
For everything you need to know about getting started, read our full Microdosing 101 Guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why did my mushroom chocolate hit harder than the same dose of dried shrooms?
Several reasons work together: the mushroom powder in chocolate is more bioavailable than whole dried mushrooms because cell walls are already disrupted; the fat matrix delivers a slower, more complete release; and cacao’s mild MAOI activity, theobromine, and anandamide may genuinely amplify the experience. All of these factors compound on top of each other.
Can I just eat more chocolate to increase the dose?
Yes, but proceed slowly. Because of the delayed onset with fat-based edibles, always wait at least 90 minutes before considering an additional dose. Rushing the redose is the number one cause of accidental overconsumption with mushroom chocolates.
Do mushroom gummies feel different from mushroom chocolates?
Yes, meaningfully so. Gummies — especially those made with psilocybin extract rather than whole mushroom powder — tend to have a faster and more consistent onset, lower nausea risk, and a cleaner come-up without the additional pharmacological contributions of cacao. The trade-off is that they may lack the entourage effect of whole-mushroom products.
Does the percentage of cacao in the chocolate matter?
It can. Higher-cacao-percentage chocolates (70%+ dark chocolate) contain more theobromine, MAOIs, and anandamide than milk chocolate formulations. If you’re eating a ceremonial-grade dark chocolate bar, you may want to start with a slightly lower mushroom dose than you would with a milk chocolate base.
Is heating the mushrooms in the chocolate making the psilocybin weaker?
This is a common concern. The melting point of cacao paste is around 94°F — well below temperatures that degrade psilocybin. Authors of the Psilocybin Chef Cookbook note there’s no hard evidence that typical chocolate-making temperatures meaningfully affect psilocybin content. The benefits of processing (cell wall disruption, reduced nausea) far outweigh any minimal thermal degradation risk in a properly made bar.
The Bottom Line
When you eat 1 gram of psilocybin mushroom chocolate, you are not having the same experience as eating 1 gram of dried mushrooms. You’re consuming a fundamentally different delivery format — one where the mushroom powder has had its cell walls disrupted for better bioavailability, where the fat matrix smooths and extends absorption, and where cacao itself is adding its own mild pharmacological layer to the experience.
The result is typically a softer onset, a longer and more sustained peak, dramatically less nausea — and often a noticeably more intense experience at the same gram weight.
Understanding this isn’t just interesting — it’s essential for dosing intelligently and staying safe. Start lower than you think you need to. Wait longer than you think you should. And respect the fact that the matrix matters as much as the molecule.
Happy tripping.
Curious to explore? Browse our full selection of magic mushrooms, mushroom chocolates, and microdose capsules — or read our full guide on How Different Strains Affect Your Experience before your next session.
Sources
- Wikipedia — Psilocybin Pharmacokinetics — https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psilocybin
- Wikipedia — Psilocybin Mushroom Dosing — https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psilocybin_mushroom
- Recovered.org — Psilocybin Edibles: Chocolate, Gummies & More — https://recovered.org/hallucinogens/psilocybin/psilocybin-edibles
- California Detox — Mushroom Chocolate Bars — https://californiadetox.com/drug-info/mushroom-chocolate-bars/
- Soul Lift Cacao — Ceremonial Cacao and Psilocybin Mushrooms — https://soulliftcacao.com/blogs/news/psilocybin-mushroooms-and-ceremonial-cacao-in-psychedelic-therapy
- Truffle Report — Stacking Psychedelics: Can Chocolate Enhance Your Trip? — https://truffle.report/stacking-psychedelics-can-chocolate-enhance-your-trip/
- Zamnesia — The Aztec Psychedelic Combo: Mixing Psilocybin With Cacao — https://www.zamnesia.com/blog-aztec-magic-mushrooms-cacao-n383
- Tripsitter — Cacao & Magic Mushrooms: Why Is This Combination So Powerful? — https://tripsitter.com/cacao-mushrooms/
- Psychedelic Science Review — Why Do Magic Mushrooms Cause Nausea? — https://psychedelicreview.com/why-do-magic-mushrooms-cause-nausea/
- Ouroboros Foundation — Psilocybin and Gastrointestinal Distress — https://www.theouroborosfoundation.org/knowledge-base/psilocybin-and-gastrointestinal-distress-what-causes-gut-issues
- Alchimia Grow Shop — Magic Mushrooms and Stomach Problems — https://www.alchimiaweb.com/blogen/magic-mushrooms-stomach-problems/
- Hamilton’s Mushrooms — Is Chitin Digestible? — https://hamiltonsmushrooms.com/blogs/the-fungible-content/is-chitin-digestible-it-in-now
Disclaimer: This blog is for educational and harm reduction purposes only and is not medical advice.


















 A Brief History of Panaeolus cyanescens
A Brief History of Panaeolus cyanescens